Are Blockchain & Big Data Analytics a perfect match?
Not so long ago, a consortium of 47 Japanese banks teamed up with a company called Ripple to facilitate cash transfers between bank accounts through blockchain. The main reason for the move was to enable real-time transfers at a very low cost. One of the reasons why traditional real-time transfers were expensive was in the potential risk factors. Dual issues (a form of transaction failure that uses the same security token twice) are a real problem in real-time transfers. Blockchain technology largely avoids this risk. Big Data Analytics makes it possible to identify patterns of consumer spending and to identify risky transactions much faster than current technology. This can significantly reduce the cost of real-time transactions.
Outside of banking, the main driving force behind the introduction of Blockchain was security. In healthcare, retail and public administration, companies have begun to use blockchain to analyze data, prevent hacking and data leakage. In healthcare, technology such as blockchain can be used e.g. Make sure that multiple “signatures” are checked at each level of data access. This may prevent a repeat of hacker attacks, such as in 2015 (read here), which resulted in the theft of over 100 million patient records.
The blockchain is currently developing into a kind of universal authentication technique.
POSSIBILITIES IN REAL-TIME ANALYSIS
So far, real-time fraud detection was just a dream, and banks have always relied on using technology to identify fraudulent transactions. Since Blockchain contains a database entry for each transaction, institutions can search for patterns in real time as needed. Companies like Chainalytics and Coinalytics use this real-time intelligence to detect anomalies early or near real-time.
Blockchain technology improves transparency in data analysis. Unlike previous algorithms, the blockchain rejects any input that cannot be verified and is considered suspicious.
OUTLOOK
Although Blockchain is promising for data science, the truth is that we do not (yet) have many blockchain-based technology systems on an industrial scale. At the moment, many companies are experimenting with Blockchain technology. In the USA and the Asian countries, one hears already of applications in the productive range which are based on the Blockchain technology. Unfortunately, Germany is lagging behind in such matters. We at AISOMA are firmly convinced that 2018 will be the year of Blockchain in Germany and expect a significant increase in the number of implementations.
For data scientists, this mainly means that it will take a while for the data treasure that Blockchain technology has to offer to be made available across various industries.
Finally, we would like to give you a brief overview of possible usage scenarios (cross-industry) of Blockchain technology.
[bctt tweet=”Blockchain & Big Data Analytics – the perfect match? #Blockchain #BigDataAnalytics #AI #ML #DataScience” username=”AISOMA_AG”]
OTHER INDUSTRIES THAT COULD BENEFIT FROM THE BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY
Supply Chain: By using a Distributed Ledger, companies within a supply chain gain visibility into shipment tracking, deliveries, and progress from other suppliers who do not have inherent trust.
Legal: “Smart Contracts” stored on the Blockchain pursue contracting parties, conditions, transfer of property and delivery of goods or services without the need for legal intervention.
Public Administration: Blockchain offers promise as a technology for storing personal identity information, criminal backgrounds and e-citizenship, authorized by biometrics.
Energy: Decentralized power transfer and distribution is possible via micro-transactions of data sent to blockchain, validated and distributed to the network while ensuring payment to the forwarder.
Food: The use of Blockchain to store food supply chain data provides improved traceability of product origin, batch processing, expiration, storage temperatures and shipping.
Retail: Secure P2P marketplaces can track P2P retail transactions, entering product information, deliveries and bills of lading through the blockchain and making payments through Bitcoin.
Healthcare: Electronic patient records, stored in a blockchain and accessed and updated through biometrics, help democratize patient data and facilitate the transfer of data between providers.
Insurance: When autonomous vehicles and other smart devices communicate with insurance providers through blockchain status updates, premium costs decrease as the need for auditing and authentication of data disappears.
Tourism: Passengers store their authenticated “single travel ID” on the Blockchain to be used instead of travel documents, ID cards, loyalty program IDs and payment details.
Education: Educational institutions could use the blockchain to store data on credentials of assessments, degrees, and transcripts.
Additional info:
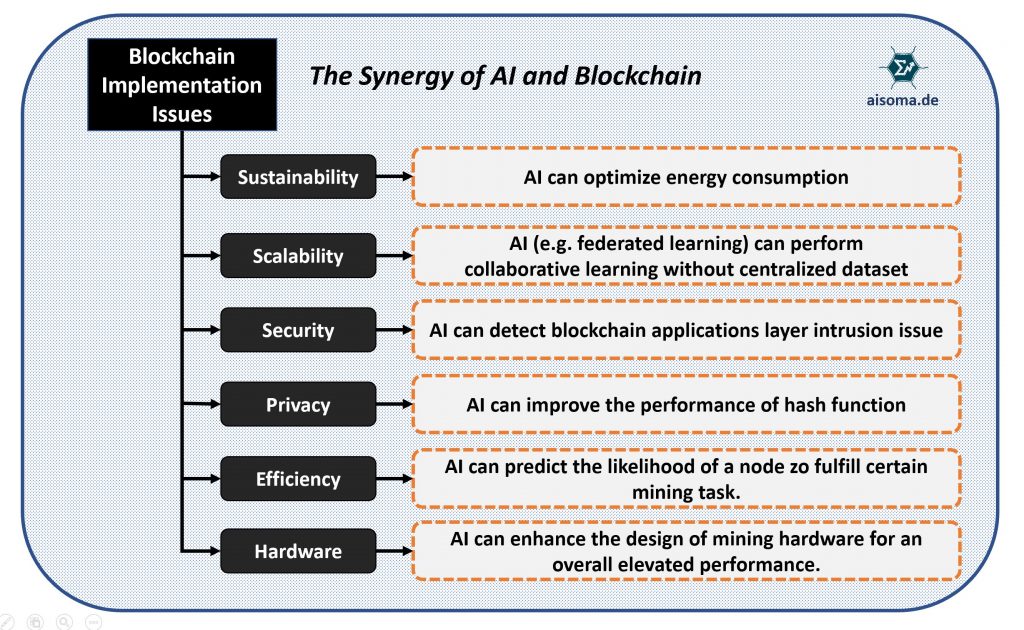
The Synergy of AI and Blockchain
Do you have any more questions?
Contact: info@aisoma.de
Further Reading: 5 Variations of Artificial Intelligence
